Ingredients
Basic Active Ingredients of kamol
Active ingredients respectively
Mode of action
Chamazulene 7-ethyl-1,4-dimethylazulene
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chamazulene exerts anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of leukotriene B4 formation (Safayhi, 1994). The en-yne dicycloether inhibits degranulation of mast cells to prevent histamine
release (Miller, 1996
Antioxidant Effects: Chamazulene have potential anti-oxidant effects. Chamazulene exerts antioxidant effects through inhibition of lipid peroxidation (Rekka,
1996). Chamazulene also blocks chemical peroxidation of arachidonic acid for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (Safayhi, 1994).
Alpha-Bisabolol 6-Methyl-2-(4-methyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-hepten-2-ol
Alpha-Bisabolol induces dose- and time-dependent apoptosis in cells via a Fas(transmembrane protein) and mitochondrial-related pathway, involves p53 and NFkappaB. NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) is a protein complex that controls the transcription of DNA.
Insight into the apoptosis-inducing action of alpha-bisabolol towards malignant tumor cells: involvement of lipid rafts and Bid protein.
Alpha-bisabolol exerts a rapid and efficient apoptosis-inducing action selectively towards human and murine malignant glioblastoma cell lines through mitochondrial damage. Apoptosis-inducing action of alpha-bisabolol towards highly malignant carcinoma cell lines without affecting human fibroblast viability.
The preferential incorporation of alpha-bisabolol to transformed cells through lipid rafts on plasma membranes and, thereafter, direct interaction between alpha-bisabolol and Bid protein, one of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, Notions that lipid rafts are rich in plasma membranes of transformed cells and that Bid, richly present in lipid rafts, is deeply involved in lipid transport make highly credible the hypothesis that the molecular mechanism of alpha-bisabolol action includes its capacity to interact with Bid protein.
Apigenin 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1benzopyran-4-one)
Apigenin, a flavonoid, effectively blocks intercellular adhesion molecule-1 upregulation and leukocyte adhesion in response to cytokines. This activity is through a mechanism unrelated to free radical scavenging or leukocyte formation (Panes, 1996).
Apigenin is a potential cancer chemo preventive agent, it inhibits proliferation of cancer cells and reduces the number, size, of skin tumors/epithelial carcinoma that develop in response to chemical cancer/UVB exposure by a mechanism involving inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase activity in DNA. The high dose of apigenin not found more effective than the low dose in the prevention of skin/epithelial carcinogenesis.
Induces the reversion of transformed phenotypes of v-H-ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells at low concentration (12.5 uM) by inhibiting MAP kinase activity. Also inhibits the proliferation of malignant tumor cells by G2/M arrest and induces morphological diffentiation.
Apigenin was a potent inhibitor of epidermal ornithine decarboxylase induction by TPA in a dose-dependent manner .Apigenin inhibited skin papillomas and showed the tendency to decrease conversion of papillomas to carcinomas.
Antineoplastic Effects:
Apigenin applied topically has effects on skin tumorigenesis through inhibition of skin papillomas and a tendency to decrease the conversion of papillomas to carcinomas (Li, 1996; Wei, 1990).
Apigenin inhibits UV-induced tumorigenesis when applied topically via G2/M and G1 cell-cycle arrest in keratinocytes (Lepley, 1996; Lepley, 1997). The chemoprevention mechanisms occur through inhibition of the
mitotic kinase activity, perturbation of cyclin B1 levels, and inhibition of protein kinase C (Lepley, 1996; Lin, 1997). Apigenin suppresses transcriptional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in macrophages, which is important for the prevention of carcinogenesis and inflammation (Liang, 1999).
Leutolin 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)- 5,7-dihydroxy-4-chromenone
Luteolin is thought to play a role in the human body possibly as an antioxidant, a free radical scavenger, a promoter of carbohydrate metabolism, or an immune system modulator. If applicable to the human condition, these characteristics may inhibit cancer mechanisms. Basic research results indicate luteolin as an anti-inflammatory agent with other potential effects on septic shock. It has been suggested for multiple sclerosis on the basis of in vitro work.
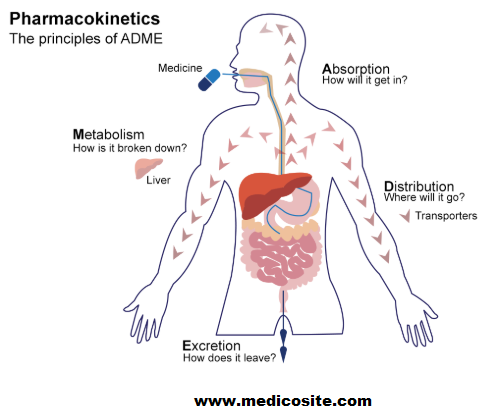
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: KAMOL did not affect iron bioavailability when administered with meals based on wheat flour and fortified with ferrous sulfate.49
Metabolism: KAMOL was investigated to observe hepatic effects on phase I and phase II metabolism. CYP1A2 metabolism was decreased significantly (p<0.05) by 39% from the control value; however, CYP2D and CYP3A were not affected. There was also no change in the activity of glutathione-s-transferases. CYP3A4 inhibition might occur withKAMOL, currently seen in vitro, which can decrease metabolism, increase serum concentration, and possibly cause drug toxicity.51
A study revealed that there are strong intersubject variations of KAMOL metabolite in urine.52 The urinary excretion of hippurae and glycine increased with depleted creatinine concentrations in some subjects. The metabolite profile persisted for two weeks after KAMOL ingestion, suggesting that the metabolic effects were prolonged two weeks after stopping daily ingestion.
Drug Interactions
Aspirin:
Aspirin may theoretically interact with KAMOL, which contains anticoagulant compounds called coumarins, and increase the risk of bleeding.
Platelet Inhibitors:
e.g. Ticlopidine (Ticlid), Clopidogrel (Plavix)
Platelet inhibitors are used to reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke and for patients who have had a coronary stent implant. KAMOL contains anticoagulant compounds called coumarins. When combined, they may increase the risk of bleeding.
Anticoagulants:
e.g. Warfarin (Coumadin)
Warfarin is derived from coumarin, a compound with anticoagulant properties also found in KAMOL.
Tricyclic Antidepressants:
e.g. Amitriptyline (Elavil, Endep), Clomipramine (Anafranil), Imipramine (Tofranil)
Tricyclic antidepressants are metabolized in the body by the enzyme CYP1A2. KAMOL has been found to inhibit CYP1A2 and may theoretically increase blood concentrations of tricyclic antidepressants, increasing the risk of toxicity.
Clozapine:
Clozapine (Clozaril, Leponex, Fazacio) is metabolized in the body by the enzyme CYP1A2. KAMOL has been found to inhibit CYP1A2 and may theoretically increase blood concentrations of Clozapine, increasing the risk of toxicity.
Propranolol:
Propranolol (Inderal)is a beta-blocker used to treat high blood pressure. It is metabolized in the body by the enzyme CYP1A2. Chamomile has been found to inhibit CYP1A2 and may theoretically increase blood concentrations of Propranolol, increasing the risk of toxicity.
Theophylline:
Theophylline (e.g. Theo-24, Theolair, Bronkodyl, Slo-bid, Slo-Phyllin, Theobid, Theo-Dur, TheolairSR, Uni-Dur) is a bronchodilator used to help people with lung conditions breathe easier. It is metabolized in the body by the enzyme CYP1A2. KAMOL has been found to inhibit CYP1A2 and may theoretically increase blood concentrations of Theophylline, increasing the risk of toxicity.
Tacrine:
Tacrine (Cognex) helps treat symptoms associated with Alzheimer's disease or dementia. It is metabolized in the body by the enzyme CYP1A2. KAMOL has been found to inhibit CYP1A2 and may theoretically increase blood concentrations of Tacrine, increasing the risk of toxicity.
Sources :
Cupp MJ and Tracy TS. "Cytochrome P450: new nomenclature and clinical implications." American Family Physician. 57.1 (1998):107-16.
Ganzera M et al. "Inhibitory effects of the essential oil of chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) and its major constituents on human cytochrome P450 enzymes." Life Sciences. 78.8 (2006):856-61.
Maliakal PP and Wanwimolruk S. "Effect of herbal teas on hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes in rats." Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 53.10 (2001):1323
The synergistic effects of kamol
Inference
KAMOL is an Anti-inflammatory Antioxidant having a specific effect of Apoptosis by the mechanism of selective cancer cell death by Mitochondrial damage at D.N.A. levels. KAMOL stops the proliferation of cancer cells / ectodermal tumors by the action of its various components. Due to its Antioxidant action it has a very good capacity to regenerate the normal epithelial cells & stop the histamine release thus decreases inflammation.
All the properties of KAMOL makes it the drug of choice in the treatment of oral stomatitis mucosistitis (chemo & radio therapy induced), leukoplakia, oral-submucous fibrosis, erosions / ulcerations of the oral cavity. KAMOL is also very effective in the cases of tonsillitis & pharyngitis.
KAMOL an oral rinse is a good, safe pleasantly flavored mouth freshener.

Contact us
+91 7880506682
We are working to cure the oral precancerous lesions from 2009 with huge nur of success stories in curing the precancerous lesions in our one decayed journey.

Contact us
+91 7880506682
We are oral cancer expert for oral precancerous lesions .Our head office is in Delhi and regional office is in Lucknow. working in this field from past 15 years. Our complete team is clinical expert .

Contact us
+91 7880506682
Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, Selective malignant cell death (i.e. Apoptosis) of Cancer/malignant transformed cells in ectodermal / epithelial Carcinoma, prevents the proliferation of cancer cells. Kamol is extensively used for the treatment of oral stomatitis, ulcers, inflammations of oral cavity, leukoplakia, oral-submucous fibrosis , oral mucosistitis, pharyngitis and oral cancer

Contact us
+91 7880506682
We are working to cure the oral precancerous lesions from 2009 with huge nur of success stories in curing the precancerous lesions in our one decayed journey.
F.A.Q
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How kamol reduces Odema?
In odema there is a breakdown of the adherens junctions between the cells lining ,the capillaries allowing fluid to leak into the tissue spaces.
Chamazulene exerts anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of leukotriene B4 formation.( Leukotriene B4 is a leukotriene involved in inflammation. It is produced from leukocytes in response to inflammatory mediators and is able to induce the adhesion and activation of leukocytes on the endothelium, allowing them to bind to and cross it into the tissue.) In neutrophils, it is also a potent chemoattractant, and is able to induce the formation of reactive oxygen species (These are produced by activated phagocytes: macrophages and neutrophils. They are toxic for microorganisms).and the release of lysosome enzymes by these cells.The granules of mast cells are loaded with histamine and their exocytosis releases this potent mediator. Histamine increases the blood flow to the area and the leakage of fluid and proteins from the blood into the tissue space. Thus the quick release of histamine produces the redness and swelling associated with inflammation. The en-yne dicycloether inhibits degranulation of mast cells to prevent histamine release. -
Mechanism of inhibition of Cycloxygenases?
Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes: These are potent mediators of inflammation and are derivatives of arachidonic acid (AA) a 20-carbon unsaturated fatty acid produced from membrane phospholipids.
The principal pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism arethe cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway, which produces prostaglandin H2 (PGH2). PGH2 serves as the substrate for two enzymatic pathways: one leading to the production of several
prostaglandins (PG); the other leading to the production of
thromboxanes (Tx).
the 5-lipoxygenase pathway, which produces a collection of leukotrienes
The body produces several different forms of cyclooxygenase (COX), including
COX-1, which is involved in pain, clotting, and protecting the stomach;
COX-2, which is involved in the pain produced by inflammation.
COX-2 inhibitors are effective against inflammation and seem to avoid damage to the GI tract. But, unfortunately, they increase the risk of blood clots — which can cause heart attacks and strokes — because they do not block the synthesis of thromboxane A2 by platelets (which contain only COX-1). So people depending on NSAIDs for their heart protective effects must monitor any use of COX-2 inhibitors carefully. -
How kamol increases granulation process?
The alpha-bisabolol promotes granulation and tissue regeneration in ulcers.Apigenin may be an anti-inflammatory constituent, due to the water-soluble and lipophilic components. The flavones block the arachidonic acid pathway by inhibiting phospholipase A, cyclo-oxygenase, and lipoxygenase pathways. chamazulene and alpha-bisabolol, have also demonstrated anti-inflammatory action by interfering with 5-lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase production.The azulene have anti-allergenic and anti-inflammatory actions.
Azulene may prevent histamine discharge from tissue by activating the pituitary-adrenal system, causing the release of cortisone, or azulene may prevent allergic seizures caused by histamine release, activating cellular resistance and speeding the process of healing. alpha bisablol accelerates wound-healing, reducing inflammation and promoting tissue granulation and regeneration. -
Why kamol is safe on ingestion?
It contains Natural flavonoid components and have no damaging effect/chemically in G.I tract.
-
How it works in O.S.M.F, leukoplakia/ pre cancerous lesion?
Alpha-bisabolol exerts a rapid and efficient apoptosis-inducing action selectively towards human and murine malignant glioblastoma cell lines through mitochondrial damage. Apoptosis-inducing action of alpha-bisabolol towards highly malignant carcinoma cell lines without affecting human fibroblast viability. Chamazulene have potential anti-oxidant effects. Chamazulene exerts antioxidant effects through inhibition of lipid peroxidation.
Apigenin is a potential cancer chemo preventive agent, it inhibits proliferation of cancer cells and reduces the number, size, of skin tumors/epithelial carcinoma that develop in response to chemical cancer/UVB exposure by a mechanism involving inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase activity in DNA. The high dose of apigenin not found more effective than the low dose in the prevention of skin/epithelial carcinogenesis.Induces the reversion of transformed phenotypes of v-H-ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells at low concentration (12.5 uM) by inhibiting MAP kinase activity. Also inhibits the proliferation of malignant tumor cells by G2/M arrest and induces morphological differentiation.
Apigenin was a potent inhibitor of epidermal ornithine decarboxylase induction by TPA in a dose-dependent manner .Apigenin inhibited skin papillomas and showed the tendency to decrease conversion of papillomas to carcinomas. Antineoplastic Effects: Apigenin applied topically has effects on skin tumorigenesis through inhibition of skin papillomas and a tendency to decrease the conversion of papillomas to carcinomas.
Apigenin inhibits UV-induced tumorigenesis when applied topically via G2/M and G1 cell-cycle arrest in keratinocytes (Lepley, 1996; Lepley, 1997). The chemoprevention mechanisms occur through inhibition of the mitotic kinase activity, perturbation of cyclin B1 levels, and inhibition of protein kinase C (Lepley, 1996; Lin, 1997). Apigenin suppresses transcriptional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in macrophages, which is important for the prevention of carcinogenesis and inflammation (Liang, 1999)
Luteolin is thought to play a role in the human body possibly as an antioxidant, a free radical scavenger, a promoter of carbohydrate metabolism, or an immune system modulator. If applicable to the human condition, these characteristics may inhibit cancer mechanisms. Basic research results indicate luteolin as an anti-inflammatory agent with other potential effects on septic shock. It has been suggested for multiple sclerosis on the basis of in vitro work. -
How kamol works in pharyngitis and tonsillitis?
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx.] In most cases it is painful. It is the most common cause of a sore throat.
Pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic. Pharyngitis can result in very large tonsils which cause trouble swallowing and breathing. Pharyngitis can be accompanied by a cough or fever, for example, if caused by a systemic infection.
Most acute cases are caused by viral infections (40–80%), with the remainder caused by bacterial infections, fungal infections, or irritants such as pollutants or chemical substances Treatment of viral causes are mainly symptomatic while bacterial or fungal causes may be amenable to antibiotics and anti-fungal respectively.
Apigenin may be an anti-inflammatory constituent19, due to the water-soluble and lipophilic components. The flavones block the arachidonic acid pathway by inhibiting phospholipase A, cyclo-oxygenase, and lipoxygenase pathways. chamazulene and a-bisabolol, have also demonstrated anti-inflammatory action by interfering with 5-lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase production20. The azulene have anti-allergenic and anti-inflammatory action.
Chamazulene exerts anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of leukotriene B4 formation Leukotriene B4 is a leukotriene involved in inflammation -
How kamol cures oral ulcer?
Alpha bisablol accelerates wound-healing, reducing inflammation and promoting tissue granulation and regeneration
Chamazulene have potential anti-oxidant effects. Chamazulene exerts antioxidant effects through inhibition of lipid peroxidation ( Chamazulene also blocks chemical peroxidation of arachidonic acid for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Luteolin is thought to play a role in the human body possibly as an antioxidant, a free radical scavenger, a promoter of carbohydrate metabolism, or an immune system modulator Chamazulene exerts anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of leukotriene B4 formation (Safayhi, 1994). The en-yne dicycloether inhibits degranulation of mast cells to prevent histamine release (Miller, 1996). Apigenin, a flavonoid, effectively blocks intercellular adhesion molecule-1 upregulation and leukocyte adhesion in response to cytokines. This activity is through a mechanism unrelated to free radical scavenging or leukocyte formation -
Role in gingivitis?
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums (gingiva).
Bleeding gums (blood on toothbrush even with gentle brushing of the teeth)
Bright red or red-purple appearance to gums
Gums that are tender when touched, but otherwise painless
Mouth sores
Swollen gums
Shiny appearance to gums
Kamol reduces inflamation of gums.Apigenin may be an anti-inflammatory constituent19, due to the water-soluble and lipophilic components. The flavones block the arachidonic acid pathway by inhibiting phospholipase A, cyclo-oxygenase, and lipoxygenase pathways. chamazulene and a-bisabolol, have also demonstrated anti-inflammatory action by interfering with 5-lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase production20. The azulene have anti-allergenic and anti-inflammatory action.
Chamazulene exerts anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of leukotriene B4 formation Leukotriene B4 is a leukotriene involved in inflammation -
Why efffective in halitosis/mouth freshner?
Antimicrobial : According to in vitro studies the essential oil has bactericidal and fungicidal activities against Gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus) and Candida albicans in concentrations above 0.05% v/v26. Extracts of chamomile have demonstrated antimicrobial activity against E. coli27. The growth of S. aureus, Streptococcus mutans and group B streptococcus was inhibited by chamomile extract at concentrations of 10 mg/ml. Complete mouth wash.
-
Cellular level mechanism of kamol in curing precancerous lesion?
KAMOL is an Anti-inflammatory Antioxidant having a specific effect of Apoptosis by the mechanism of selective cancer cell death by Mitochondrial damage at D.N.A. levels. KAMOL stops the proliferation of cancer cells / ectodermal tumors by the action of its various components. Due to its Antioxidant action it has a very good capacity to regenerate the normal epithelial cells & stop the histamine release thus decreases inflammation.All the properties of KAMOL makes it the drug of choice in the treatment of oral stomatitis mucosistitis (chemo & radio therapy induced), leukoplakia, oral-submucous fibrosis, erosions / ulcerations of the oral cavity. KAMOL is also very effective in the cases of tonsillitis & pharyngitis. KAMOL an oral rinse is a good, safe pleasantly flavored mouth freshener.
